A laser printer uses heat, light, and powdered toner to create quick, clean, and sharp prints. It’s great for text and documents. Laser printers use a laser beam to create an image. Then, they permanently fuse toner onto the page. This is different from inkjet printers, which spray liquid ink onto paper. This makes them a popular choice for homes, offices, and businesses that need reliable, high-volume printing with consistent quality.
If you’ve ever wondered what a laser printer is, how it works, or whether it’s the right choice for your needs, this guide breaks everything down in simple, beginner-friendly language. You’ll discover how laser printers and inkjet printers differ. You’ll learn what each type is best for, their running costs, and the main pros and cons to think about before buying. No technical terms or sales pressure.
How Does a Laser Printer Work? (Step-by-Step, Easy Version)
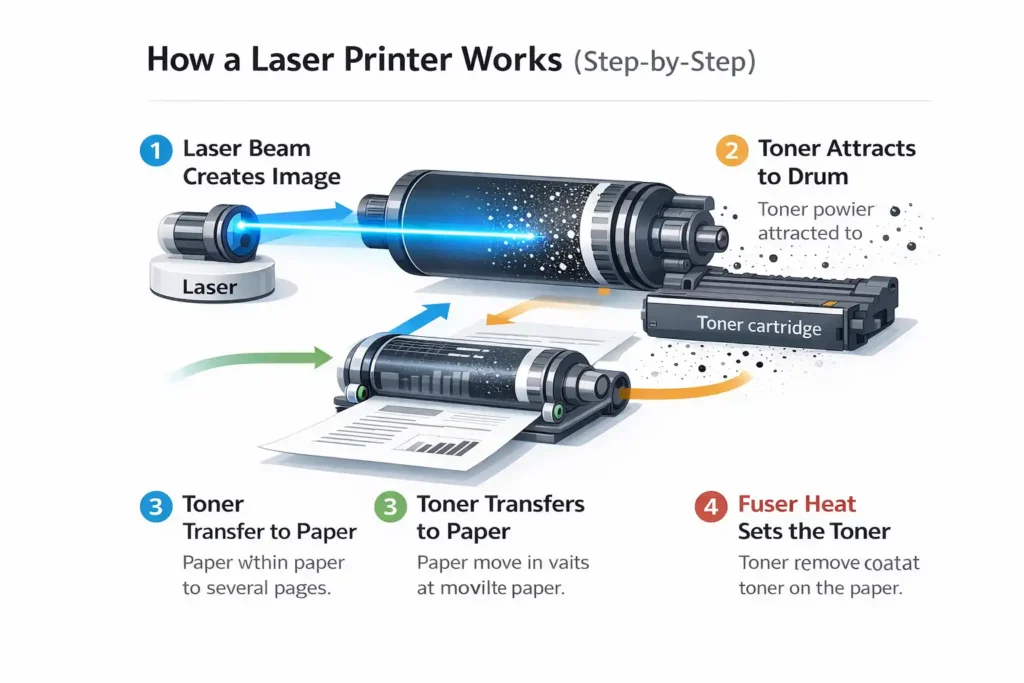
A laser printer creates clear, dry, and smudge-free prints by using light, heat, and powdered toner. While the inside may sound complex, the process itself is simple when explained step by step. A laser printer works differently from an inkjet printer. Instead of spraying liquid ink, it uses a laser beam and a toner cartridge. This method allows it to place text and images onto paper quickly and accurately.
Below is a beginner-friendly breakdown of how a laser printer works from start to finish.
Step 1: Creating the Image with a Laser
The process starts when you send a print command from your computer or phone. A laser beam inside the printer scans a rotating drum. It “draws” the shape of the text or image you want to print.
This laser beam changes the electrical charge on the drum, but only in the areas where the image should appear. Think of it like drawing invisible letters with light. This step is what makes a laser printer so precise, especially for text.
This is very different from an inkjet printer, which pushes liquid ink through tiny nozzles in a cartridge.
Step 2: Toner Attraction to the Drum
Next, the toner cartridge releases very fine toner powder. This toner sticks only to the charged areas on the drum that were created by the laser beam.
Because toner is dry powder, it does not soak into the paper like ink from an inkjet printer cartridge. This is why a laser printer produces sharp text with clean edges.
In a color laser printer, this step happens separately for each color, allowing the printer to combine them accurately.
Step 3: Transferring Toner to Paper
Once the toner is sitting on the drum in the correct shape, the paper moves through the printer. The drum rolls over the paper and transfers the toner onto it.
At this stage, the toner is resting on the paper, but is not permanent yet. If you touched it now, it could smudge. This is true for both black-and-white laser printer models and color laser systems.
Step 4: Heat Fuses Toner Permanently
In the final step, the paper passes through heated rollers called a fuser. These rollers melt the toner and press it firmly into the paper fibres.
This heat-based process is why prints from a laser printer come out dry immediately. There is no waiting time, unlike some inkjet printers that may smear before drying.
This step also explains why laser printers use more power during printing than an inkjet printer, but deliver faster results.
Do you need to understand the technical parts? (Short Answer: No)
You do not need to understand drums, fusers, or internal parts to use a laser printer. Modern laser printers are designed to work automatically. You simply replace the toner cartridge when needed and load paper.
For everyday users, whether at home, school, or the office, a laser printer is reliable, low-maintenance, and easy to operate. Even advanced models like a color laser printer or color laser multifunction device work with the same basic process every time.
What Does a Laser Printer Use Instead of Ink?
A common question many beginners ask is whether a laser printer uses ink like other printers. The simple answer is no. Laser printers use toner, which is a dry powder, not liquid ink. This key difference makes laser printers fast and clean. They are perfect for offices and homes that print frequently.
A laser printer doesn’t push ink from a cartridge. Instead, it uses a laser to apply toner directly onto the paper. Then, it seals the toner with heat. This method reduces smudging and delivers consistent results, especially for text-heavy documents.
What Is Toner Powder?
Toner powder is a very fine, dry substance made from plastic particles and pigment. In a laser printer, toner is kept in a cartridge. It’s released in controlled amounts when printing.
When the printer receives a print command, it uses a laser to form an image on a drum. The toner sticks to this image and then transfers onto the paper, where heat permanently fuses it. This process explains why printed pages come out dry and ready to use immediately.
Toner powder is best for printing documents, reports, and high volumes. It’s all about speed and reliability, not glossy images.
Toner vs Ink: Key Differences Explained Simply
Toner and ink serve the same purpose, but they work in very different ways. The table below explains the main differences in simple terms:
| Feature | Toner (Laser Printers) | Ink (Inkjet Printers) |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Dry powder | Liquid |
| Storage | Toner cartridge | Ink cartridge |
| Drying time | Instant | May take time |
| Best for | Text and documents | Photo printing |
| Smudging | Rare | More likely |
| Use case | Office and business | Home and photo use |
Laser printers work with toner, so they create sharp details in both colour and black-and-white prints. Inkjet printers are great for photo printing. However, they need more frequent cartridge changes.
Why Toner Lasts Longer Than Ink Cartridges
Toner cartridges generally have a longer lifespan than ink cartridges. This is because they print more pages. A single toner cartridge can often print thousands of pages, while an ink cartridge may run out after a few hundred.
This higher page yield leads to a lower cost per page, which is why many offices prefer laser printers for regular use. Toner does not dry out like liquid ink, so it stays usable even if the printer sits unused for weeks.
Laser printers rely on toner. It’s efficient, long-lasting, and saves money on daily printing. This makes them a smart choice for users who need reliable output without constant cartridge changes.
(Text, Images, and Graphics)
Print quality is one of the biggest reasons people compare inkjet vs laser options. While both printer types can produce good results, they do so in different ways. Understanding how laser printing handles text, images, and graphics will help you choose the right printer for your needs.
Why Laser Printers Produce Sharp Text
Laser printers generally produce sharper text than inkjet printers, making documents look professional. The printing process uses electrical charges and heat. This helps place toner powder exactly on the page. The printer uses a laser beam to define each letter before fusing it permanently.
As a result, the text looks crisp, even in small font sizes. This is why legal offices, schools, and businesses prefer a monochrome laser printer for documents.
In simple terms, this is a key difference between laser and ink-based printing. Inkjet printers use liquid ink, which can spread slightly on paper. Laser printers do not have this problem, so letters stay sharp.
How Laser Printers Handle Images and Photos
Laser printers can print images and charts clearly. However, they aren’t made for high-quality photo output. Laser printers can print diagrams, graphs, and logos very well, especially on standard paper.
Inkjet printers usually excel at photo printing. They use liquid ink, which blends colours smoothly. Laser printers focus more on speed and accuracy than color depth.
This difference is important when comparing inkjet and laser printers for mixed use.
Color Laser Printers vs Photo Printers
A color laser printer is excellent for business graphics, charts, and everyday color printing. It prints fast, resists smudging, and handles large workloads well.
Photo printers, which are usually inkjet-based, are built for detailed images and glossy paper. They use special inks to create smooth color transitions.
Here is a simple comparison to show the difference between laser and inkjet quality:
| Feature | Color Laser Printer | Photo (Inkjet) Printer |
|---|---|---|
| Best for | Documents, charts | Photos |
| Printing speed | Fast (high pages per minute) | Slower |
| Ink type | Toner powder | Liquid ink |
| Paper type | Plain paper | Photo paper |
| Use case | Office and school | Photography |
Laser printers offer reliability and speed, while photo printers focus on image detail.
DPI Explained Without the Technical Confusion
DPI means dots per inch. It sounds technical, but the idea is simple. DPI shows how much detail a printer can place on paper.
Laser printers often have lower DPI numbers than inkjets, yet still produce sharp text. This is because of how printers work internally. The laser-based system places toner very accurately, so a higher DPI is not always needed.
For everyday documents, DPI differences rarely matter. Most users will not notice a quality gap in normal printing needs.
Who Should Use a Laser Printer? (Is It Right for You?)
Choosing a printer depends on how and how often you print. Laser printers offer speed and efficiency, but they are not perfect for everyone.
Laser Printers for Home Users
Home users who print bills, homework, or forms can benefit from laser printers. They are reliable and do not dry out like ink-based models.
The initial cost might be higher than some inkjet models. So, casual users should think about how often they print.
Laser Printers for Students
Students who print notes and assignments regularly will find laser printers helpful. A monochrome laser model is cost-effective over time. It can print often without slowing down.
Laser printers offer clean text and low maintenance, which suit academic use.
Laser Printers for Small Offices
Small offices often need fast output and consistent quality. Laser printers are ideal because they support high-volume printing and deliver steady performance.
Many offices compare inkjet and laser printers. They often choose laser printers because they have lower running costs in the long run.
Laser Printers for High-Volume Businesses
Businesses with heavy printing needs rely on laser printers. These printers often deliver high pages per minute, handle large print queues, and require fewer supply changes.
Laser printers offer long-term savings despite a higher upfront cost.
Who Should NOT Buy a Laser Printer (Honest Advice)
Laser printers may not suit users who mainly print photos or need rich color detail. People who print occasionally may also find inkjet printers more affordable.
If image quality matters more than speed, inkjet printers use ink better suited for that purpose.
Inkjet printers tend to be slower and more expensive per page, but they are better for photo printing.x
Types of Laser Printers
Laser printers come in different designs to match different needs. Understanding these printer types makes choosing the right printer easier.
Monochrome Laser Printers (Black & White Only)
A monochrome laser printer prints only in black and white. It is fast, cost-efficient, and perfect for text documents.
A monochrome laser model is often the first choice for offices and students who do not need color.
Color Laser Printers
Color laser printers print both black-and-white and color documents. They are best for presentations, charts, and business graphics.
Laser printers can print color efficiently, but they focus more on clarity than photo realism.
Single-Function vs All-in-One Laser Printers
Single-function printers only print. All-in-one models can print, scan, copy, and sometimes fax.
All-in-one laser printers offer convenience for offices and homes with varied printing needs.
Final Perspective
When comparing laser and inkjet printers, the best type of printer depends on usage. Laser printers are great for users with lots of documents. Inkjet models work well for creative and photo tasks.
Understanding the difference between laser and inkjet technology helps you choose a printer that matches your needs, budget, and long-term goals.
Advantages of Laser Printers
A laser printer is a type of printer that uses modern printer technology to deliver fast and reliable results. Many offices and schools use laser printers because they are efficient and consistent. Below are the main benefits explained in simple terms.
Fast Printing Speed
Laser printers are known for their speed. A laser printer uses a laser and an electrostatic process to quickly print text on paper. Laser printers print a full page at once, so they are faster than ink-based models.
This makes them ideal for offices that need to handle printing tasks without delays. When printing large documents, laser printers typically finish the job in minutes.
Low Cost Per Page
One of the several advantages of laser printers is the lower cost per page. Laser printers use toner powder instead of liquid ink, which lasts longer.
Over time, this saves money, especially for users who print often. This is a major reason why businesses prefer laser printers over other printers designed for light home use.
High Print Volume Capability
Laser printers are built for heavy workloads. Printers are typically designed to handle hundreds or even thousands of pages per month without slowing down.
Laser printers are great for offices, schools, and copy centres. They support continuous printing, so they are very reliable. Inkjet printers often struggle with this level of demand.
Clean, Smudge-Free Output
A laser printer produces dry prints instantly. The toner is fused using heat, so there is no wet ink. As a result, laser printers produce clean pages that do not smear.
This is helpful when printing reports, forms, or documents that need to look professional.
Minimal Day-to-Day Maintenance
Laser printers typically require less daily care. They do not clog or dry out like ink-based machines. Laser printers use toner cartridges, which last a long time and are easy to replace.
Because of this, printers tend to need less attention from users.
Disadvantages of Laser Printers
While laser printers provide many benefits, they are not perfect. Honest drawbacks help users choose the right printer with confidence.
Higher Upfront Cost
Laser printers usually cost more at the start. The laser printer’s purchase price is often higher than that of an inkjet model.
Although running costs are lower, the initial price can be a barrier for casual users.
Not Ideal for Photo Printing
Laser printers are not the best choice for photos. Inkjet printers often deliver smoother colors and better detail for images.
If you mainly want to print photos, an inkjet printer is likely a better choice than a laser printer. A comparison of inkjet printers often focuses on documents.
Size and Weight Considerations
Laser printers are usually larger and heavier. Printers usually have more internal parts, like drums and fusers, so they weigh more.
This makes them less portable than smaller inkjet models.
Power Consumption Compared to Inkjet
Laser printers use heat to fuse toner, which requires more electricity. Inkjet printers often consume less power, especially for light use.
This difference matters for home users with low print volumes.
How Much Does a Laser Printer Really Cost to Run?
Understanding real running costs helps to build trust and authority. Below is a clear breakdown based on real-world usage.
Cost Per Page Explained with a Simple Example
A laser printer may print around 2,000 pages using one toner cartridge. If the cartridge costs $80, each page costs about $0.04.
Laser printers are cheaper to run than most inkjet printers. This makes them a good choice for frequent use.
Toner Yield and Replacement Costs
Laser printers use toner powder, which does not dry out. Toner cartridges often last for months, even with regular printing.
This reliability is one reason why offices rely on laser printers.
Electricity Usage and Power Consumption
Laser printers consume more power during printing because of the heat. However, they print faster, so total energy use balances out for high-volume users.
For occasional printing, inkjet models may use less electricity.
Long-Term Cost Comparison: Laser vs Inkjet
| Factor | Laser Printers | Inkjet Printers |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront cost | Higher | Lower |
| Running cost | Lower | Higher |
| Cartridge life | Long | Short |
| Best for | Frequent printing | Occasional use |
This table shows why businesses prefer laser printers over ink-based options.
Laser Printer vs Inkjet Printer (Quick Comparison)
This section highlights the difference that printer buyers care about most.
Speed
Laser printers are faster because they use an electrostatic method. This helps them process pages quickly.
Print Quality
Laser printers focus on sharp text, while inkjet printers focus on image detail.
Cost Over Time
Laser printers save money in the long term due to toner efficiency.
Maintenance
Inkjet printers often need cleaning. Laser printers do not clog.
Best Use Cases
Laser printers suit offices and schools. Inkjet printers suit homes and photographers.
So, always when deciding between an inkjet vs laser printer, consider print speed, cost per page, and document types.
Common Laser Printer Problems (and How to Fix Them)
Even reliable machines can have issues. Knowing quick fixes builds confidence.
Lines or Streaks on Printouts
This often means the drum or toner needs cleaning or replacement. Wipe gently and check the cartridge.
Faded or Light Prints
Low toner levels usually cause this. Replace the toner cartridge to restore quality.
Toner Smudging Issues
Smudging may occur if the fuser is not heating properly. Restart the printer and allow it to warm up.
Paper Jams and Feeding Problems
Remove the paper slowly and check for torn pieces. Use the correct paper type.
Ghosting or Repeated Images
Ghosting happens when old images reappear faintly. This usually means the drum is worn and needs replacement.
Final Expert Note
A laser printer is a type of printer that uses a laser and laser light to create sharp, fast, and reliable prints. Laser printing is an electrostatic process that suits users with frequent printing needs.
Both laser printers and inkjet printers have strengths. Choosing the right one depends on usage, budget, and long-term goals.
How to Maintain a Laser Printer (Simple User Tips)
Laser printers are reliable, but a little care can make them last longer and work better. Most laser printers come ready for heavy use and do not need daily attention. Still, basic maintenance can reduce breakdowns, lower printing costs, and keep print quality consistent.
What You Should Clean (And How Often)
You should clean only the parts that users can safely access. These include the paper tray, output tray, and exterior surfaces.
Dust and loose toner can build up over time. Wipe these areas gently with a dry, lint-free cloth every few weeks. This helps the printer handle paper smoothly and prevents jams.
Laser printers usually need less cleaning than ink-based ones. This is because they do not use liquid ink, which can leak or dry out.
What You Should Never Touch
Avoid touching internal components such as the drum, fuser, or rollers. These parts are sensitive and can be damaged by the oils from your hands.
Do not expose the drum to direct light. The printing process relies on light control, where a laser beam projects an image during printing. Touching or exposing parts can reduce print quality.
If you are unsure, it is always safer to close the printer and follow the user manual.
When to Replace Toner and Drum Units
Most laser printers alert users when the toner is low. Replace the toner when prints start to fade or streak.
Some printers have separate drum units. Replace the drum when the printer warns you or when print quality drops. Laser printers tend to use these parts efficiently, so replacements are not frequent.
Laser printers are built for heavy use, so their parts often outlast those in many home printers.
Storage and Environmental Tips
Place the printer in a clean, dry room with good airflow. Avoid high humidity and direct sunlight.
Printers can accommodate different paper types, but always store paper flat and dry. Proper storage improves feeding and print consistency.
Laser printers, unlike inkjet models, aren’t affected by ink drying. This makes them easier to store when not in use.
Are Laser Printers Safe to Use?
Safety is a common concern, especially in homes and offices. Laser printers meet strict safety standards, so they are safe for regular use.
Is Toner Powder Dangerous?
Toner powder is sealed inside cartridges and does not easily escape. Under normal use, it poses no health risks.
If a spill happens, avoid sweeping or vacuuming with a household vacuum. Wipe gently with a damp cloth. Modern laser printers are much safer than older models.
Heat and Ventilation Concerns
Laser printers use heat to fuse toner to paper. This is part of how printing is an electrostatic digital process.
During heavy use, the printer may feel warm. Place it in a well-ventilated area. Inkjet printers usually run cooler. However, they can have maintenance problems, such as clogging.
Laser Printer Safety Myths Explained
Some people believe laser printers release harmful radiation. This is not true. The laser stays inside the printer and never escapes.
Others worry about ozone or fumes. Modern laser printers tend to produce very low emissions, well within safety limits.
When deciding between an inkjet and a laser printer, safety should not be a concern. Both printer types are safe when used correctly.
Final Expert Insight
Laser printers are reliable, low-maintenance machines designed for long-term use. With basic care and proper placement, they remain safe, efficient, and cost-effective for homes and offices alike.
Laser Printer vs Modern Printing Alternatives
When considering a printer or a laser printer, it’s important to compare them with other modern printing options. Different types of printers fit different needs. By understanding laser printer technology, you can make a better choice.
Laser vs Ink Tank Printers
Ink tank printers are designed for high-volume printing at a low running cost. Inkjet printers are typically slower than laser printers and require more frequent refills.
| Feature | Laser Printer | Ink Tank Printer |
|---|---|---|
| Printing Speed | Fast | Moderate |
| Cost Per Page | Low | Very Low |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Moderate (refill required) |
| Best Use | Offices, schools | Small businesses, home offices |
| Image Quality | Good for graphics, text | Good for images, photos |
Key Point: Laser printers may offer faster speeds and professional-looking text, while ink tank printers are ideal for photo printing and very high-volume color printing.
Laser vs Thermal Printers
Thermal printers work by applying heat to special paper. They are best for your printing, like receipts, labels, or shipping tags, not general document printing.
| Feature | Laser Printer | Thermal Printer |
|---|---|---|
| Printing Method | Uses a laser beam to create an image on paper | Heat-sensitive paper |
| Speed | High | Very high for small prints |
| Running Cost | Low | Very low |
| Use Case | Documents, charts | Receipts, labels |
Key Point: Laser printers are versatile, while thermal printers are specialized for small, fast, and cost-efficient prints.
Laser vs All-in-One Printers
All-in-one printers combine printing, scanning, copying, and sometimes faxing. A laser vs all-in-one comparison shows that laser printers are faster for text-heavy work, but all-in-one devices provide convenience.
| Feature | Laser Printer | All-in-One Printer |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Very high | Moderate to high |
| Function | Print only | Print, scan, copy, fax |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Slightly higher |
| Cost | Higher upfront | Variable, depends on type |
Key Point: If you only need high-speed printing, a laser printer may be enough. If you need multiple functions, an all-in-one printer might be the better choice.
Laser Printer Buying Checklist (Before You Buy)
Before purchasing a printer or a laser printer, consider the following factors. This checklist ensures you pick the right model for your printing needs.
Monthly Print Volume
Estimate the number of pages you print each month. Laser printers are known for producing large volumes efficiently. Pick a printer that fits your volume. This helps to avoid wear and cuts printing costs.
Monochrome or Color
Decide whether you need only black-and-white prints or color as well. Laser printers may cost more for color models, but they handle business graphics, charts, and professional documents effectively.
Duplex Printing
Automatic double-sided printing saves paper and is useful for reports. Laser printers may offer duplex printing, but some models require manual flipping.
Wi-Fi and Network Support
For shared office spaces, see if the printer has Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or mobile printing. This ensures all users can send print jobs easily.
Toner Availability and Cost
Verify that toner cartridges are easy to buy and affordable. Laser printers might cost more at first, but their low running costs make them cheaper in the long run.
Common Myths About Laser Printers (Debunked)
Many people have misconceptions about laser printers. Let’s clear up the most common myths.
Laser Printers Are Only for Offices
Home users who print often can benefit from laser printers, just like businesses do. They’re quick, easy to care for, and perfect for school projects, home offices, and personal papers.
Laser Printers Are Too Expensive
Laser printers may cost more upfront, but the cost per page is often lower than inkjet printing. Over time, this makes them more cost-efficient, especially for high-volume users.
“Laser Printers Can’t Print Images”
Laser printers create clear graphics and charts. A colour laser printer can also manage colour printing. While they may not match a high-end photo printer, they are perfectly capable of producing quality images for most business and personal needs.
This section addresses common doubts, builds trust, and helps readers feel confident when deciding between an inkjet or laser printer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a laser printer is a type of printer that uses a laser beam to create sharp, fast, and reliable prints. Unlike inkjet printers, which tend to use liquid ink, laser printers generally rely on toner cartridges and an electrostatic digital printing process to produce text and graphics efficiently. These printers are great for home and office use. They support high-volume printing and can handle hundreds of pages. Plus, they need less maintenance.
When choosing between
An inkjet and a laser printer, think about
What you need. Inkjet printers are great for detailed photo prints. On the other hand, laser printers are faster and cheaper for clean document printing. Knowing the difference between a printer and an inkjet printer helps you pick the right one. This choice matters for school, business, or personal use.
Laser printers deliver professional-quality prints with ease. They’re a wise choice for anyone who prints often.
Frequently Asked Question
1. Do laser printers need ink?
No, laser printers don’t use liquid ink. They use toner powder, which fuses to the paper with heat, giving sharp, smudge-free prints.
2. Can laser printers print on any paper?
Laser printers work best on standard office paper. Special papers like glossy, thick, or cotton require checking your printer’s specs first.
3. How many pages can a laser printer print?
A single toner cartridge can often print thousands of pages, making laser printers ideal for home, office, or business use with frequent printing.
4. Can you use cotton paper in a laser printer?
Some cotton papers are safe, but always check your printer’s instructions. Cotton paper is thicker and heat-sensitive, so using it incorrectly may damage the printer.
5. What should you never do when working on a laser printer?
Never touch the drum, fuser, or internal rollers. These parts are delicate and can be damaged by oils from your hands or direct light.
